Having a virtual machine can be useful for a variety of purposes, such as testing unknown software in an isolated environment that is separate from your host operating system. A virtual machine can also help you to run incompatible software that doesn’t work with your host operating system, or simply exploring a new operating system altogether. For instance, you could have a fully working Linux inside Windows, etc. Running an operating system inside an other operating system is easy to do with virtualization software like VMware and VirtualBox.
This tutorial will focus on running Ubuntu inside a Windows host using VMware.
1. Required
A working installation of VMware Workstation Player and a Ubuntu image are required before starting the installation.
2. Create virtual machine
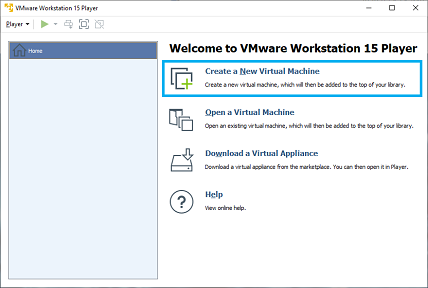
Select create a new virtual machine
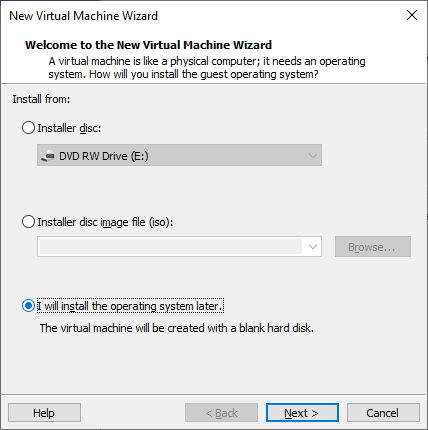
Select I will install the operating system later. Do this to avoid the easy installation.
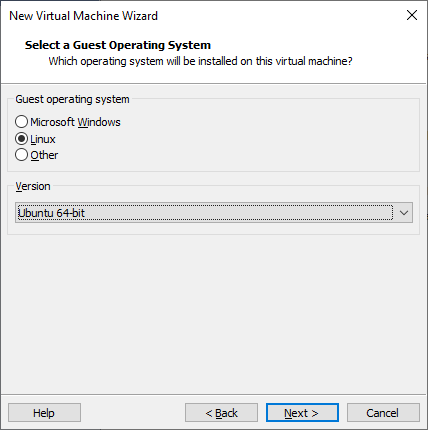
Select Linux
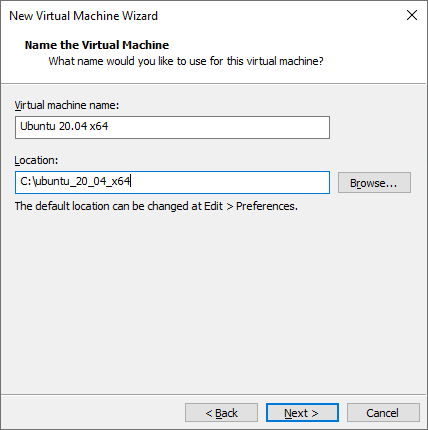
Enter the Virtual machine name and Location to install
Enter the Maximum disk size. This parameter depends on what you will do with the virtual machine, the available disk space will be the Maximum disk size minus the Ubuntu installation size.
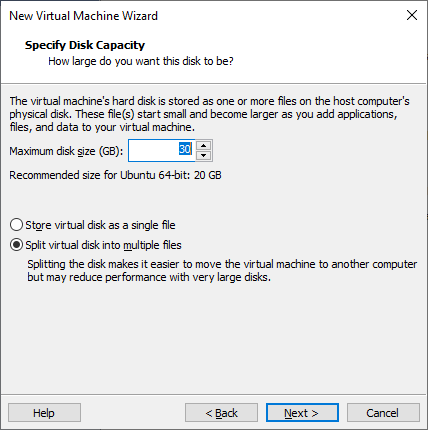
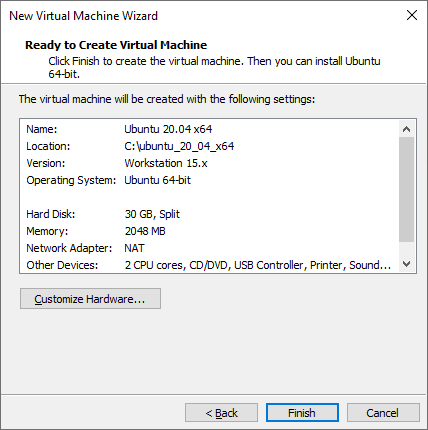
Select Customize Hardware
Change the Memory Size
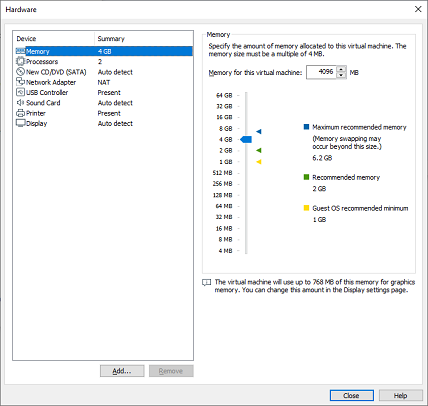
Change the Memory Size
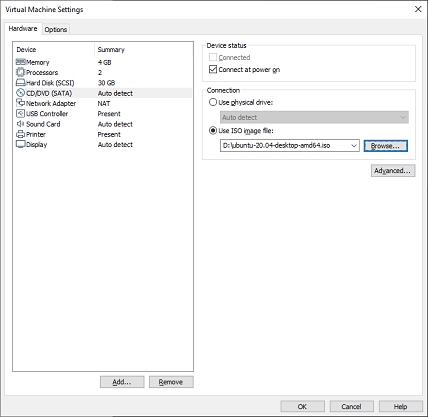
Select the Ubuntu image
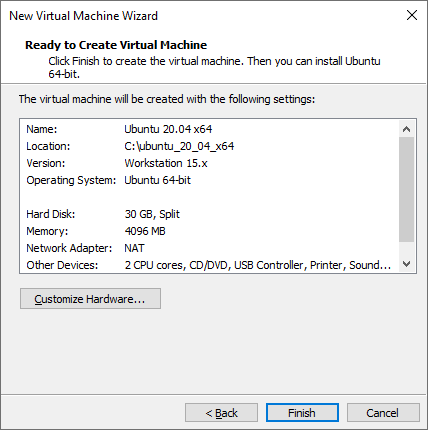
3. Install Ubuntu
Start the installation
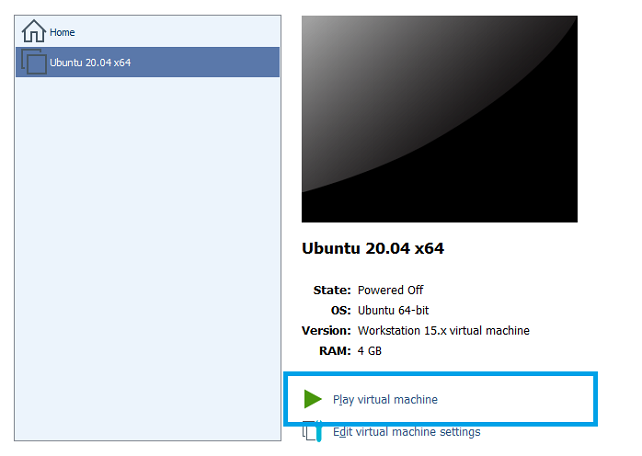
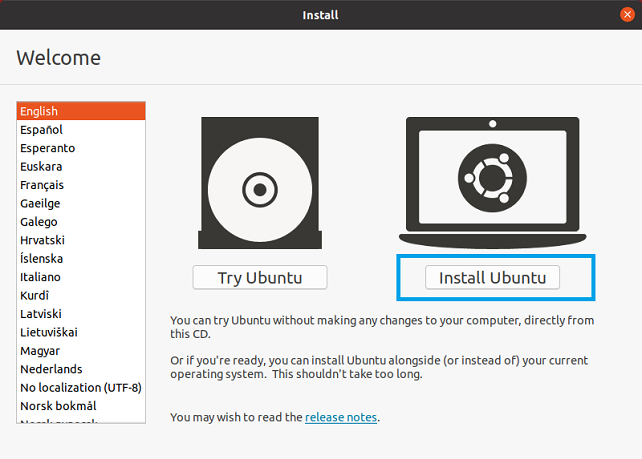
Select Install Ubuntu
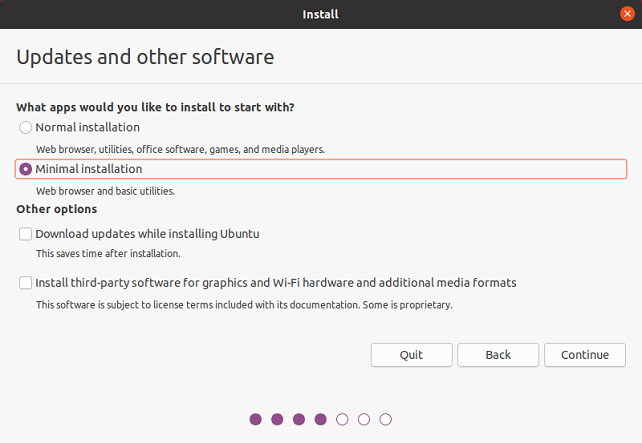
Configure Updates and other software
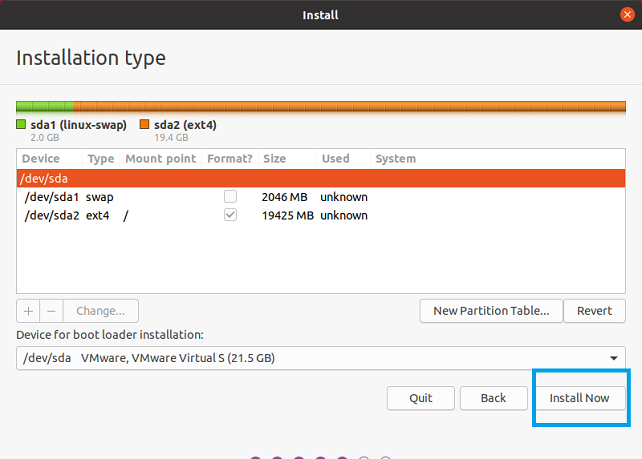
Select Installation type
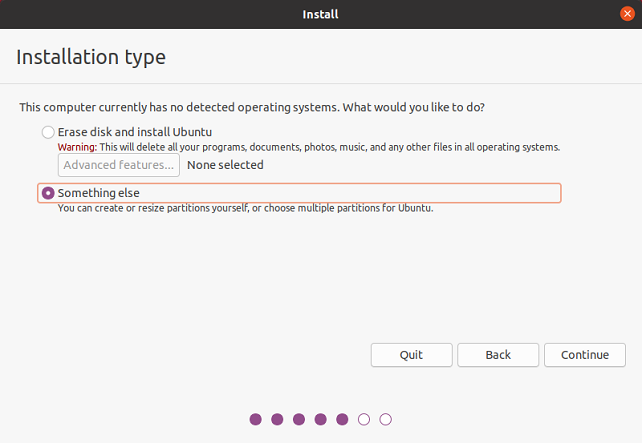
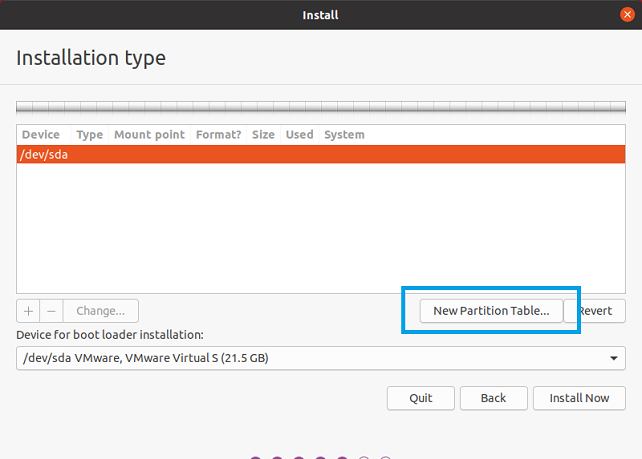
Select New Partition Table
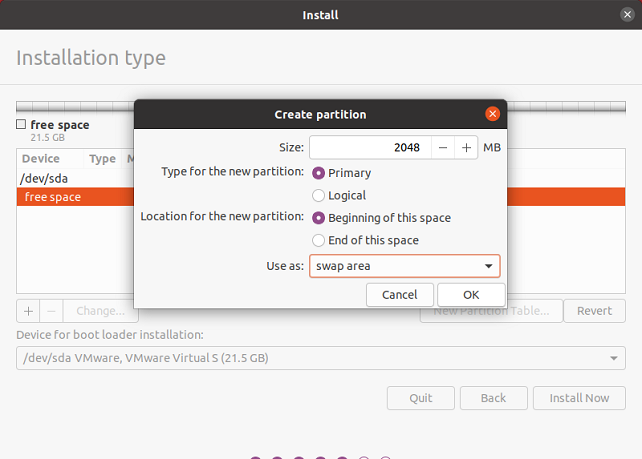
Create swap partition at the beginning of the disk.
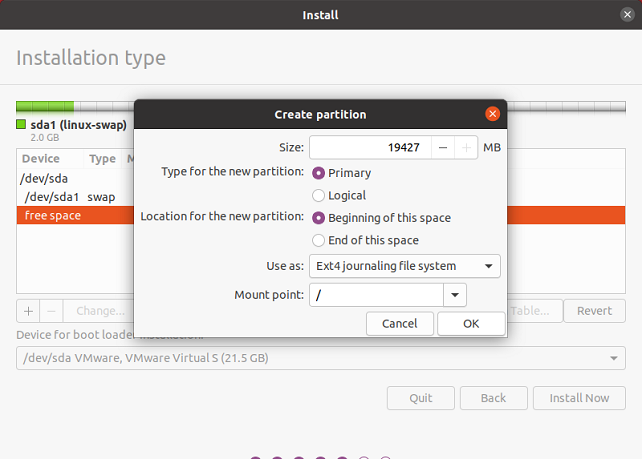
Create ext4 partition.
If you create your partitions, with the details above, you should have no issues expanding the ext4 partition.
Select Install Now
Finish the installation and boot into your newly created Ubuntu Virtual Machine.

